 |
Structural Bioinformatics Library
Template C++ / Python API for developping structural bioinformatics applications.
|
 |
Structural Bioinformatics Library
Template C++ / Python API for developping structural bioinformatics applications.
|

Authors: F. Cazals and G. Carriere
This package implements seeding methods, i.e. initialization methods for clustering algorithms, such as k-means. These methods provide seeds, namely initial positions for 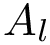
The topic was revisited in a series of papers, including [128] [21] and our own work [carriere2025improved].
This package provides implementations of these recent, methods, which can also be used to provide initial positions for components in mixture models.
We provide implementations for two kind of methods. Selection methods select seeds using no prior information. Reselection methods select refined seeds using a set of previous seeds as prior information. Reselection methods are meant to be used after a first selection to improve the seeding quality for an added runtime cost. All selection and reselection methods in this package have static runtime as a function of the dataset size, i.e. the methods are not convergence based.
Let 

The seed selection methods provided in this package include:
Random seed selection.
Seeds are obtained by selecting 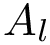
Minimax seed selection.
The first seed is obtained by selecting a single data point uniformly at random. The following 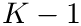
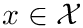

Greedy K-means++ seed selection.
Greedy K-means++ is a variant of K-means++, an initialization scheme for K-means described in [12].
K-means++ obtains the first seed by selecting a single data point uniformly at random. The following 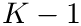
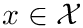

Greedy K-means++ is a simple improvement on K-means++, in which multiple candidates data points are sampled at each step, and the one candidate that minimizes 
We provide the amount of seed candidates to sample as parameter, such that sampling one candidate reduces the method to "classical" K-means++.
The seed reselection methods provided in this package include:
Greedy K-means++ seed reselection
Greedy K-means++ reselection follows the reselection scheme described in [carriere2025improved].
The method obtains 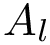
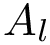
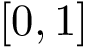
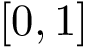
Greedy K-means++ seed reselection using centers of mass SSE.
Greedy K-means++ reselection with centers of mass SSE is a variant of greedy K-means++ reselection, differing on the seed selection metric from the pool of candidates.
Let 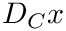
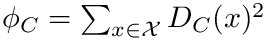
The package provides three functor classes for implementing selectors. The Cost type should be a functor class implementing the squared distance to be used. For example, in Euclidean K-means the Cost functor should output the squared Euclidean distance between two points. The three classes are :
In regards to seeding quality, using SBL::GT::T_Seed_selector_k_means_plus_plus with n_local_trials set to 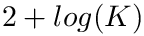
The package provides the functor class SBL::GT::T_Seed_reselector<PointType, VectorType, Cost, Candidate_metric_calculator> to implement reselectors. The operator () function of this functor admits an additional parameter n_local_trials as in the greedy K-means++ selector functor. The package also provides two functor classes to be used as template parameter for Candidate_metric_calculator, implementing the different reselection methods:
In regards to seeding quality, using SBL::GT::T_com_inertia_calculator as Candidate_metric_calculator, and setting n_local_trials to 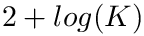
The functor classes defined in this package are templated to adapt to different contexts. In the following we describe the template parameters shared by these classes :
The (re)selectors defined above are used in the implementation of SBL::GT::T_Cluster_engine_k_means algorithm – package Cluster_engines .